Daten Interator
📘 Brick Data Iterator – Developer Guide
With the Brick Data Iterator, you can repeat its nested child bricks dynamically.
From a programming perspective, it behaves like a for-loop that iterates over an array of data.
🔁 Example
Following Example will show How to Render Multiple Tables Based on an Array.
Designer
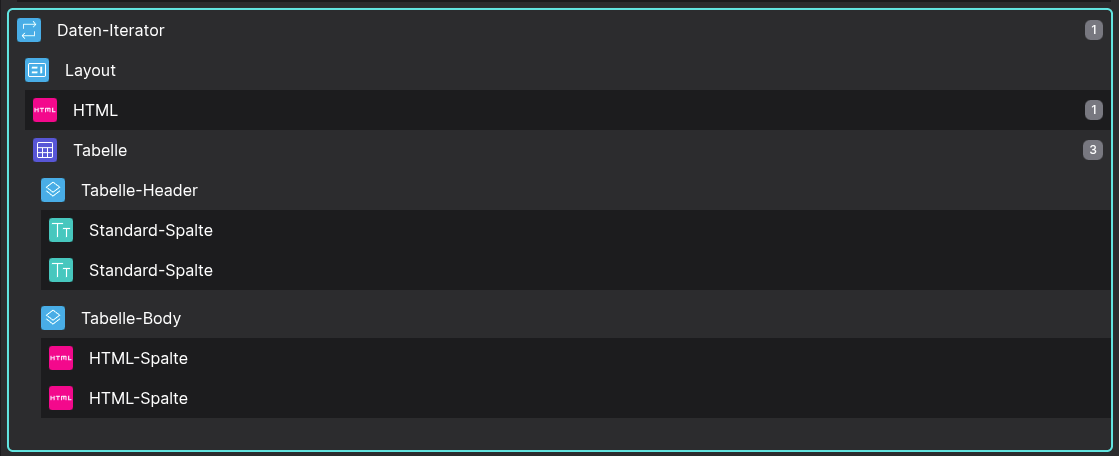
Example of a Data Iterator Brick that renders multiple tables with a headline.
Runtime
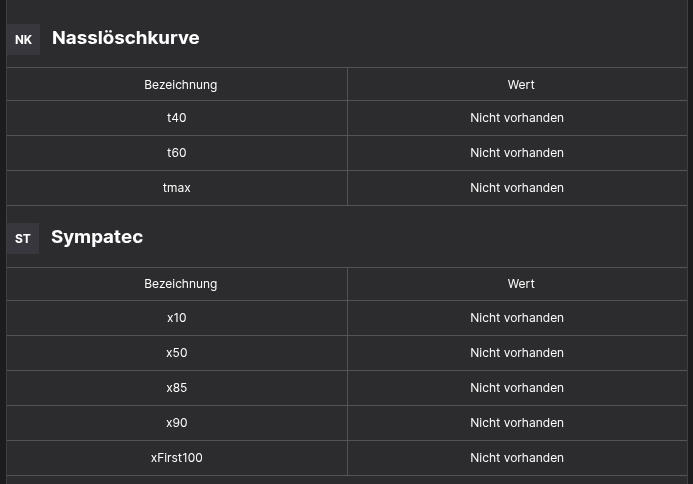
Example of how the Data Iterator Brick renders multiple tables.
⚙️ Configuration Properties
| Key | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
data |
Array of elements | Accepts an array of objects to iterate over |
entryContextKey |
Name of each item (usage see 2.2) | Variable name to access each object during iteration |
🛠️ Usage
1. Static Data
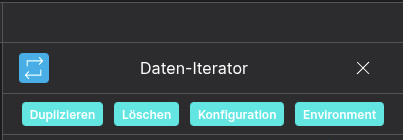
Use the configuration button to insert your static data in JSON format.
{
"data": [
{ "firstName": "Max", "lastName": "Mustermann" },
{ "firstName": "Max", "lastName": "Mustermann" }
]
}
This static data example will make your brick render its children 2 times.
2. Programmatical Data
2.1 pre-execution script of the data-iterator brick
This will make your Data Iterator render all children two times. Each time your children can access the data of the x-th element (see 2.2).
// 📥 Import required Flyze Brick APIs
const { api: brickApi } = fyzBrick;
// ⚙️ Retrieve the current configuration of the Brick
const brickConfig = brickApi.getConfig();
// 📊 Define the data to be injected into the Brick
const data = [
{ firstName: "Max", lastName: "Mustermann" },
{ firstName: "Peter", lastName: "Woodfire" }
];
// 🧩 Assign the custom data to the Brick's config
brickConfig.data = data;
// ✅ Apply the updated configuration to the Brick
brickApi.setConfig(brickConfig);
2.2 how to access data in a child brick
This example shows how to access the runtime environment of a Brick, specifically retrieving the data of the current iteration context. To make this script work you need to create an pre-execution script on your child brick.
// 📥 Import the Brick environment API
const { env: brickEnv } = fyzBrick;
// 🔍 Access the current entry's context (i.e., the x-th element in iteration)
// with entryContextKey is 'item'
const { value: item } = brickEnv.getProp('item');
// with entryContextKey is unset
const { value: entryContext } = brickEnv.getProp('entryContext');
// get all available data
const { value: item } = brickEnv.get();